设计模式
Singleton
通过保证一个 class 只有一个 instance,使得全局可以访问同一个 instance
基本型
- 构造函数是 private 的,因此外部不能使用 new 来创建 instance
- 提供一个 static 方法来访问 instance,实现全局可访问
- 第一次调用时通过 private 构造函数创建 instance
- instance 是 static 和 private 的
public class ParkingLot {
private static ParkingLot _instance = null;
private List<Level> levels;
private ParkingLot() {
levels = new ArrayList<>();
}
public static ParkingLot getInstance() {
if (_instance == null) {
_instance = new ParkingLot();
}
return _instance;
}
}
线程安全型
- synchronized 关键字确保某一时间只有一个线程可以调用 instance,其他线程需要等待
- 缺点是性能较差,需要等待
public class ParkingLot {
private static ParkingLot _instance = null;
private List<Level> levels;
private ParkingLot() {
levels = new ArrayList<>();
}
public static synchronized ParkingLot getInstance() {
if (_instance == null) {
_instance = new ParkingLot();
}
return _instance;
}
}
State Design Pattern
某些变量决定了几种特定的状态
例如 vending machine 有以下几种状态
- HAS_SELECTION
- NO_SELECTION
- COINS_INSERTED
- VENDING
与上述 state 相关的变量有
- select item
- insert coin
- execute transaction
- cancel transaction
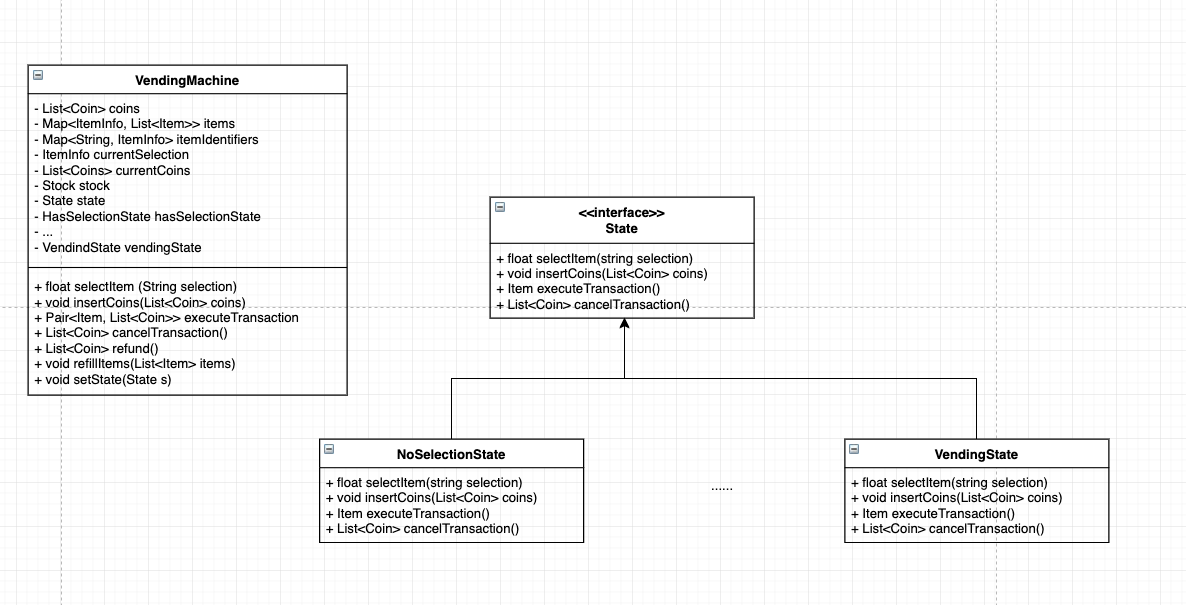
public class VendingMachine{
private AbstractState state; // current state
private NoSelectionState noSelectionState;
private HasSelectionState hasSelectionState;
private InsertedMoneyState insertedMoneyState;
public VendingMachine() {
noSelectionState = new NoSelectionsState(this); // 把自己放进去
hasSelectionState = new HasSelectionState(this);
insertedMoneyState = new InsertedMoneyState(this);
state = noSelectionState;
}
// 更改状态
public void changeToNoSelectionState() {
state = noSelectionState;
}
// 更改状态
public void changeToHasSelectionState() {
state = hasSelectionState;
}
// 更改状态
public void changeToInsertedMoneyState() {
state = insertedMoneyState;
}
public void selectItem(String selection) {
state.selectItm(selection);
}
public void addMoney(int value) {
state.insertMoney(value);
}
public void executeTransaction() {
state.executeTransaction();
}
public int cancelTransaction() {
return state.cancelTransaction();
}
}
public class NoSelectionState implements AbstracState {
VendingMachine vendingMachine;
public NoSelectionState(VendingMachine vendingMachine) {
this.vendingMachine = vendingMachine;
}
@Override
public void SelectItem(String selection) {
vendingMachine.setSelectedItem(selection);
vendingMachine.changeToHasSelectionState(); // 改变状态
}
@Override
public void addMoney(int value) {
}
@Override
public void executeTransaction() {
}
@Override
public int cancelTransaction() {
}
}
Decorator Design Pattern
Decorator pattern allows a user to add new functionality to an existing object without altering its structure. It comes under structural pattern as this pattern acts as a wrapper to existing class.
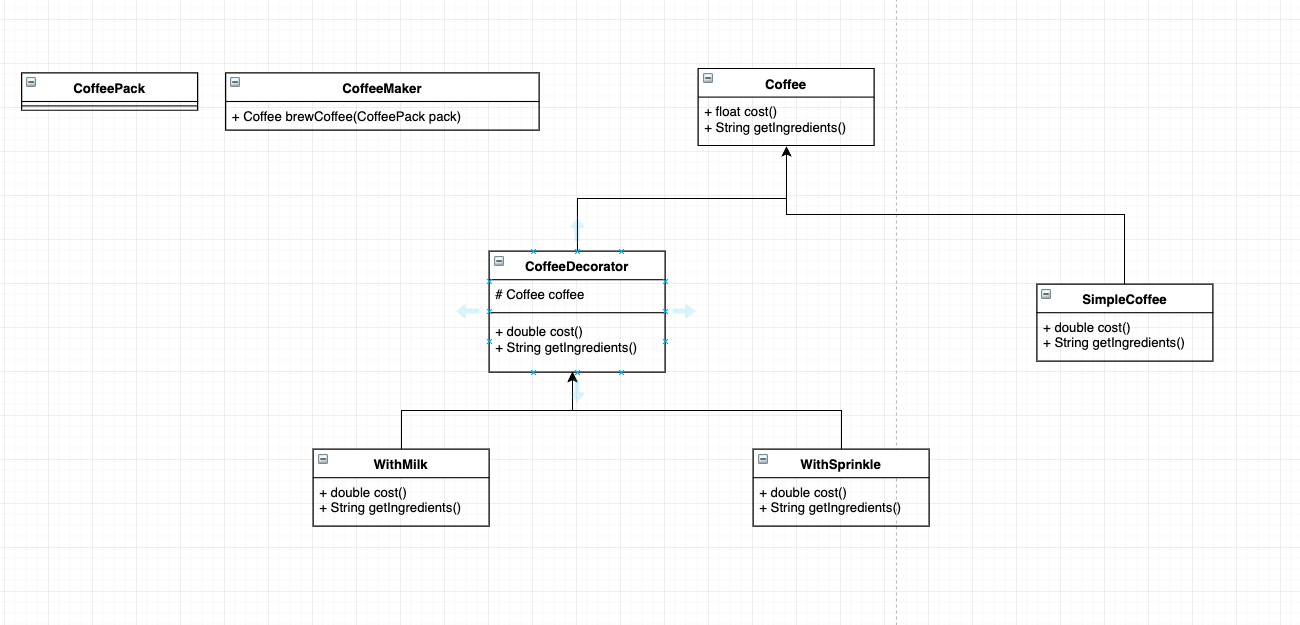
public interface Coffee {
public double getCost();
public String getIngredients();
// 普通coffee
public class SimpleCoffee implements Coffee {
@Override
public double getCost() {
return 1;
}
@Override
public String getIngredients () {
return "Coffee";
}
}
// decorator
public abstract class CoffeeDecorator implements Coffee {
protected final Coffee decoratedCoffee;
public CoffeeDecorator(Coffee c) {
this.decoratedCoffee = c;
}
public double getCost() {
return decoratedCoffee.getCost();
}
public String getIngredients() {
return decoratedCoffee.getIngredients();
}
}
// two real decorators
public WithMilk extends CoffeeDecorator {
public WithMilk (Coffee c) {
super(c);
}
public double getCost() {
return super.getCost() + 0.5; // 得到父类的价格,再加上奶的价格
}
public String getIngredients() {
return super.getIngredients() + ", Milk";
}
}
public WithSprinkles extends CoffeeDecorator {
public WithMilk (Coffee c) {
super(c);
}
public double getCost() {
return super.getCost() + 0.2;
}
public String getIngredients() {
return super.getIngredients() + ", Sprinkles";
}
}
// 主函数
public class Main {
public static void printInfo(Coffee c) {
System.out.println("Cost: " + c.getCost() + "; Ingredients: " + c.getIngredients());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Coffee c = new SimpleCoffee();
c = new WithMilk(c);
c = new WithSprinkles(c);
}
}
}
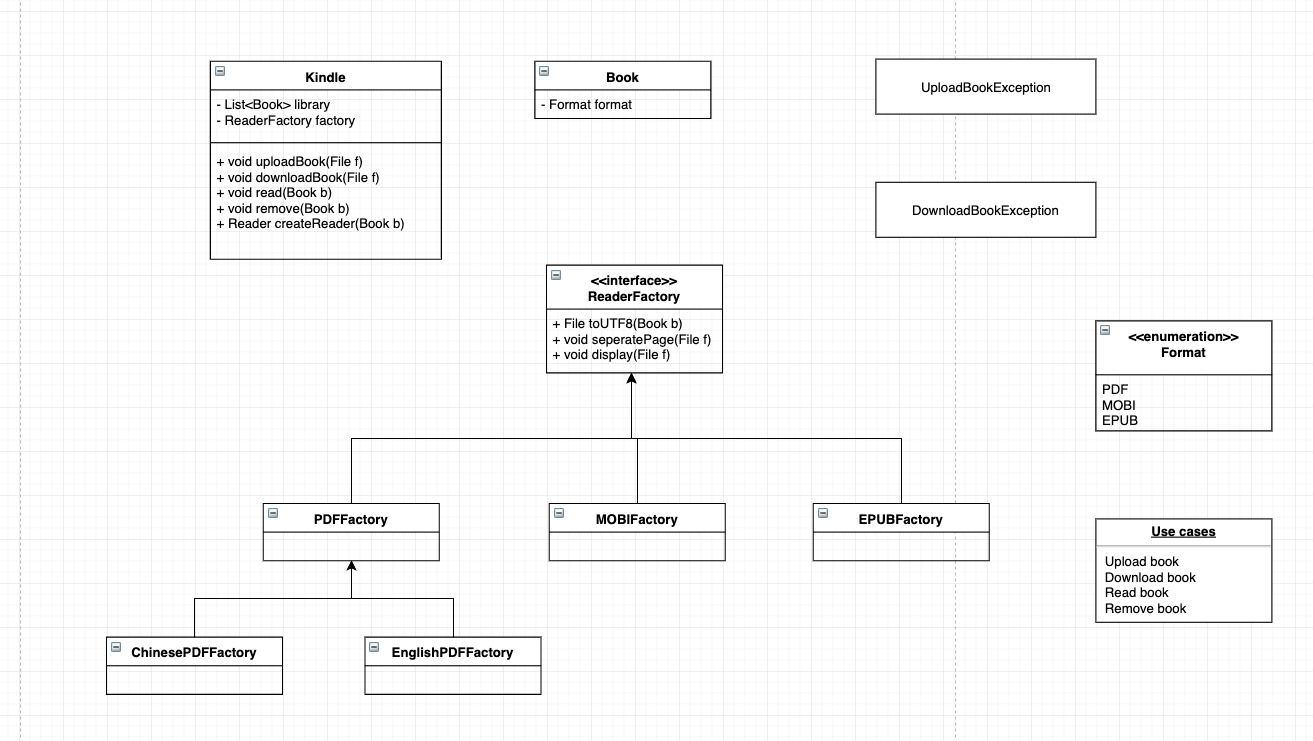
Factory Design Pattern
simple factory
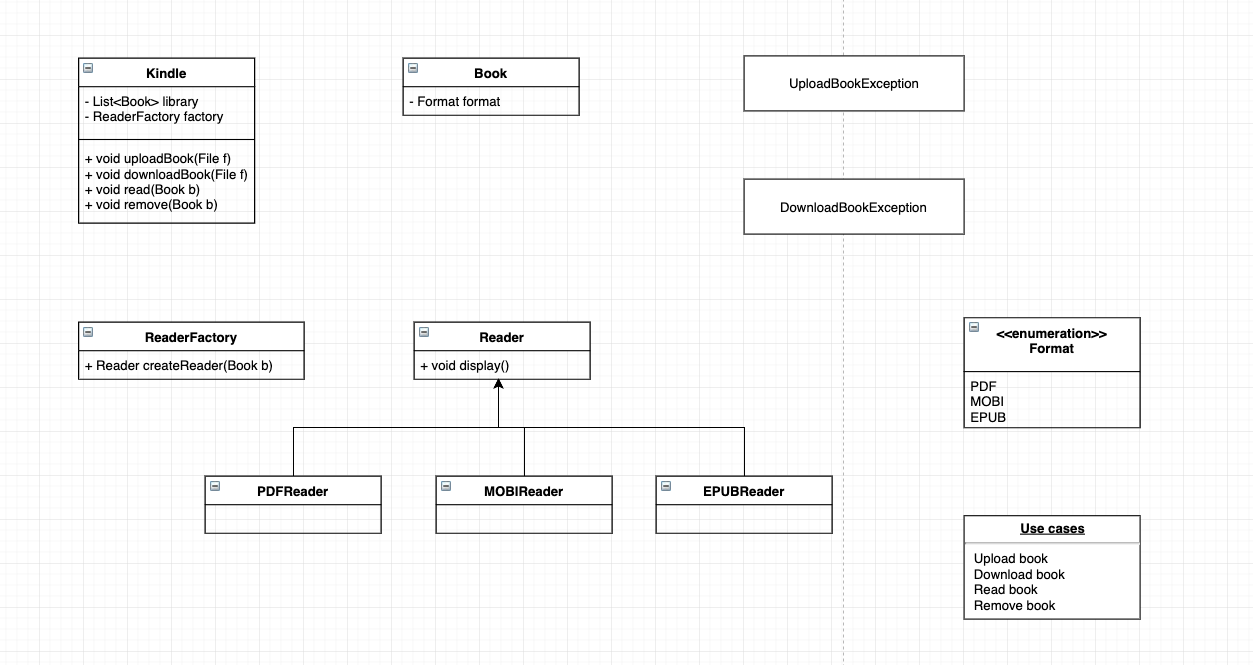
Factory method
类似加盟店一样,每一个 kindle 都继承一个方法用来生成 reader
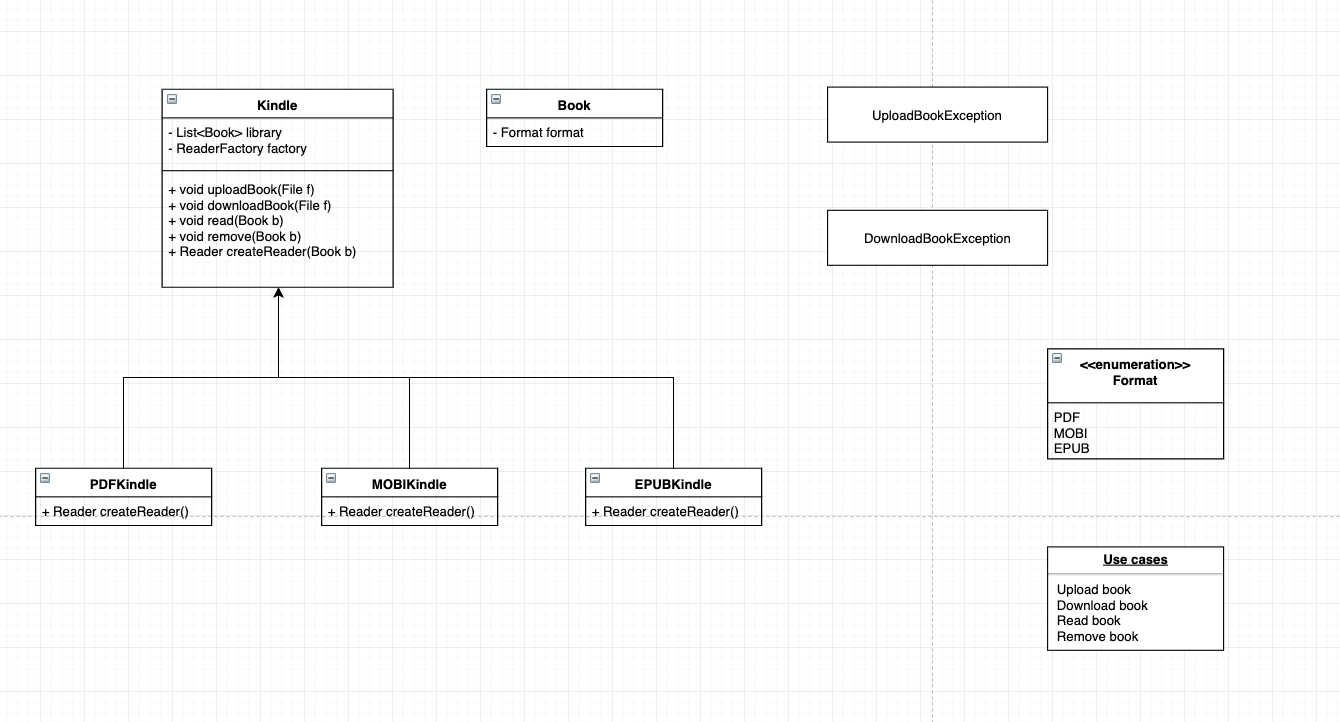
Abstract factory
抽象化工厂,适用于比较复杂的情况
Strategy Design
Strategy 是一种行为方式(behavior); 而 factory 通常用来进行初始化
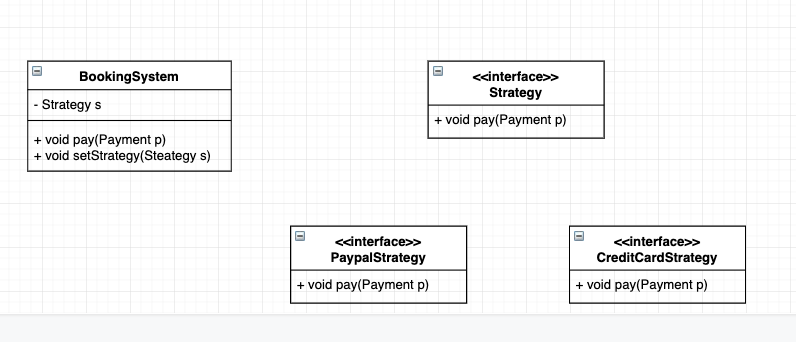
public class StrategyFactory {
public Strategy createStrategy(Payment payment) {
if (payment.getMethod().equals("paypal")) {
strategy = new PaypalStrategy();
} else if (payment.getMethod().equals("credit card")) {
strategy = new CreditCardStrategy();
}
}
}
public void pay(Payment payment) {
strategy = createStrategy(payment);
strategy.processPayment(payment);
}
public interface Strategy {
public void processPayment(Payment payment);
}
public class PaypalStrategy implements Strategy {
public void processPayment(Payment payment) {
// get paypal username
// get paypal password
}
}
public class CreditCardStrategy implements Strategy {
public void processPayment(Payment payment) {
// get credit card id
// get credit card name
// get credit card cvv
}
}