| ID | Title | Difficulty | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loading... | |||
429. N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal
Medium
LeetCode
Tree, Breadth-First Search
·
Problem
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:
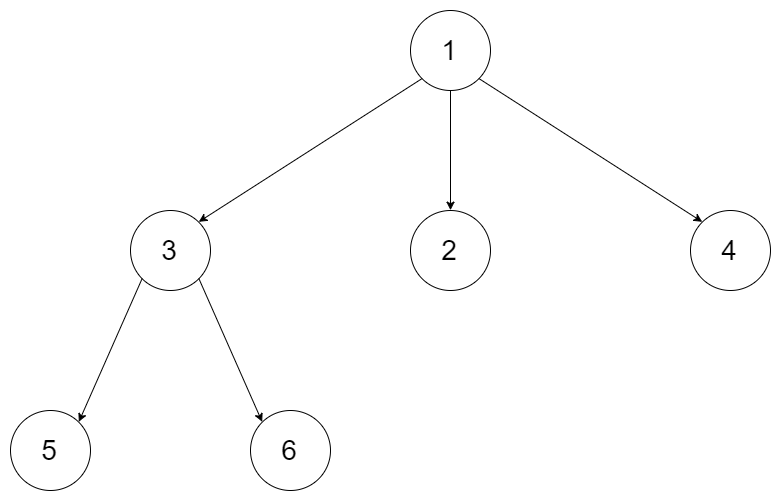
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
Example 2:
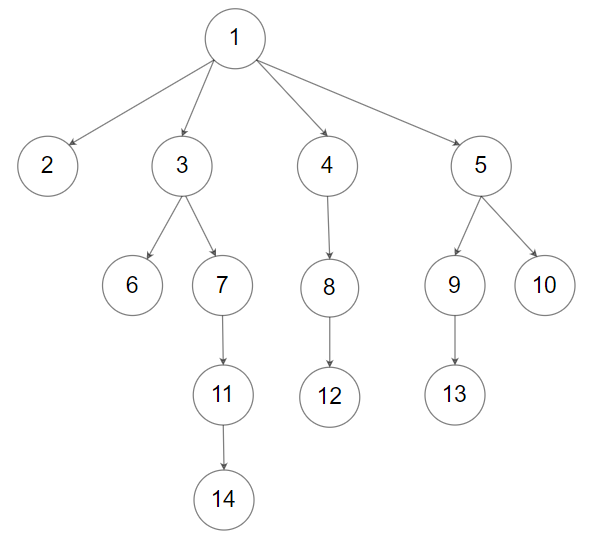
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]
Code
/**
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return res;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> curr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node node = queue.poll();
curr.add(node.val);
for(Node child : node.children) {
queue.offer(child);
}
}
res.add(curr);
}
return res;
}
}
按 <- 键看上一题!
427. Construct Quad Tree
按 -> 键看下一题!
430. Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List


