| ID | Title | Difficulty | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loading... | |||
310. Minimum Height Trees
Problem
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. In other words, any connected graph without simple cycles is a tree.
Given a tree of n nodes labelled from 0 to n - 1, and an array of n - 1 edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between the two nodes ai and bi in the tree, you can choose any node of the tree as the root. When you select a node x as the root, the result tree has height h. Among all possible rooted trees, those with minimum height (i.e. min(h)) are called minimum height trees (MHTs).
Return a list of all MHTs’ root labels. You can return the answer in any order.
The height of a rooted tree is the number of edges on the longest downward path between the root and a leaf.
Example 1:
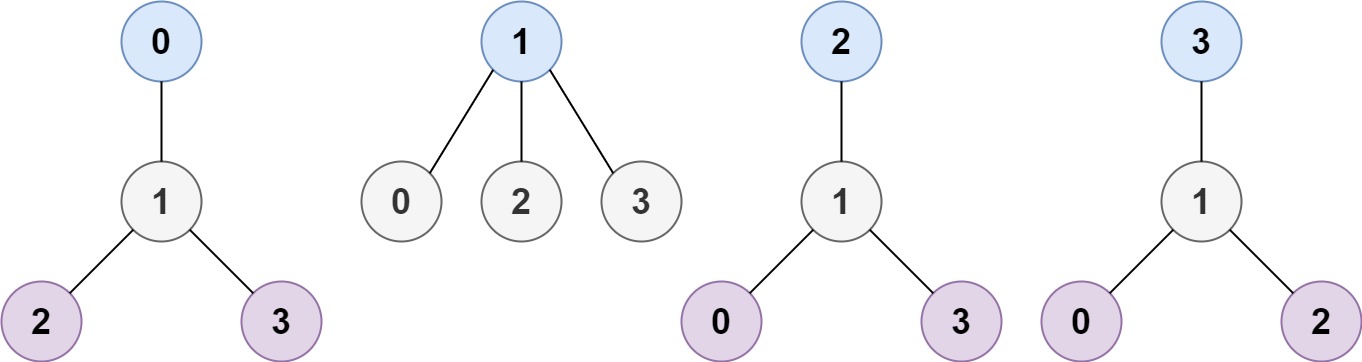
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,0],[1,2],[1,3]]
Output: [1]
Explanation: As shown, the height of the tree is 1 when the root is the node with label 1 which is the only MHT.
Example 2:
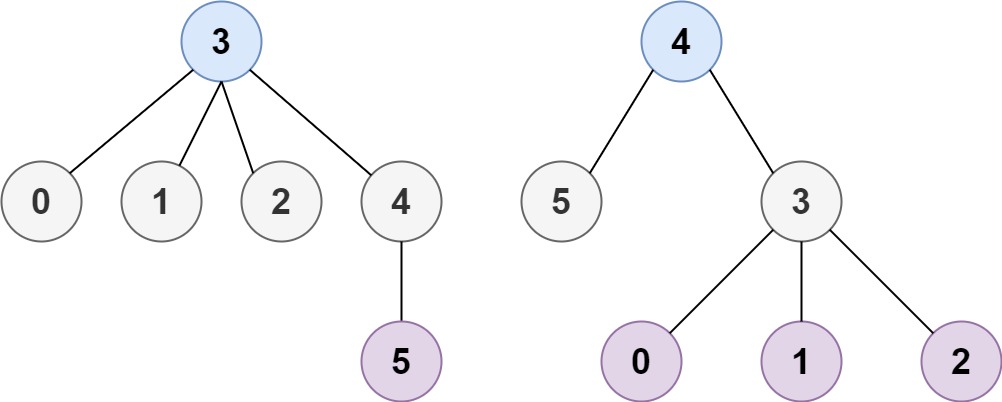
Input: n = 6, edges = [[3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4]]
Output: [3,4]
Example 3:
Input: n = 1, edges = []
Output: [0]
Example 4:
Input: n = 2, edges = [[0,1]]
Output: [0,1]
Code
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(edges == null || edges.length == 0){
res.add(0);
return res;
}
List<HashSet<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
graph.add(new HashSet<>());
}
for(int[] edge : edges){
graph.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
graph.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++){
if(graph.get(i).size() == 1){
res.add(i);
}
}
while(n > 2){
n -= res.size();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int node : res){
for(int sub : graph.get(node)){
graph.get(sub).remove(node);
if(graph.get(sub).size() == 1){
temp.add(sub);
}
}
}
res = temp;
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution:
def findMinHeightTrees(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
if n == 1:
return [0]
graph = defaultdict(set)
for edge in edges:
graph[edge[0]].add(edge[1])
graph[edge[1]].add(edge[0])
res = []
# 找到最初的叶子节点
for node in graph:
if len(graph[node])== 1:
res.append(node)
# 每次删除当前树的所有叶子节点
# 至少也要有三个点才能进行删除
while n >= 3:
n -= len(res)
leaves = []
for curr_leave in res:
# 相邻的点
adj_nodes = graph[curr_leave]
for adj_n in adj_nodes:
# 删除叶子节点
graph[adj_n].remove(curr_leave)
# 产生了新的叶子节点
if len(graph[adj_n]) == 1:
leaves.append(adj_n)
res = leaves
return res


